What is Osteoarthritis?
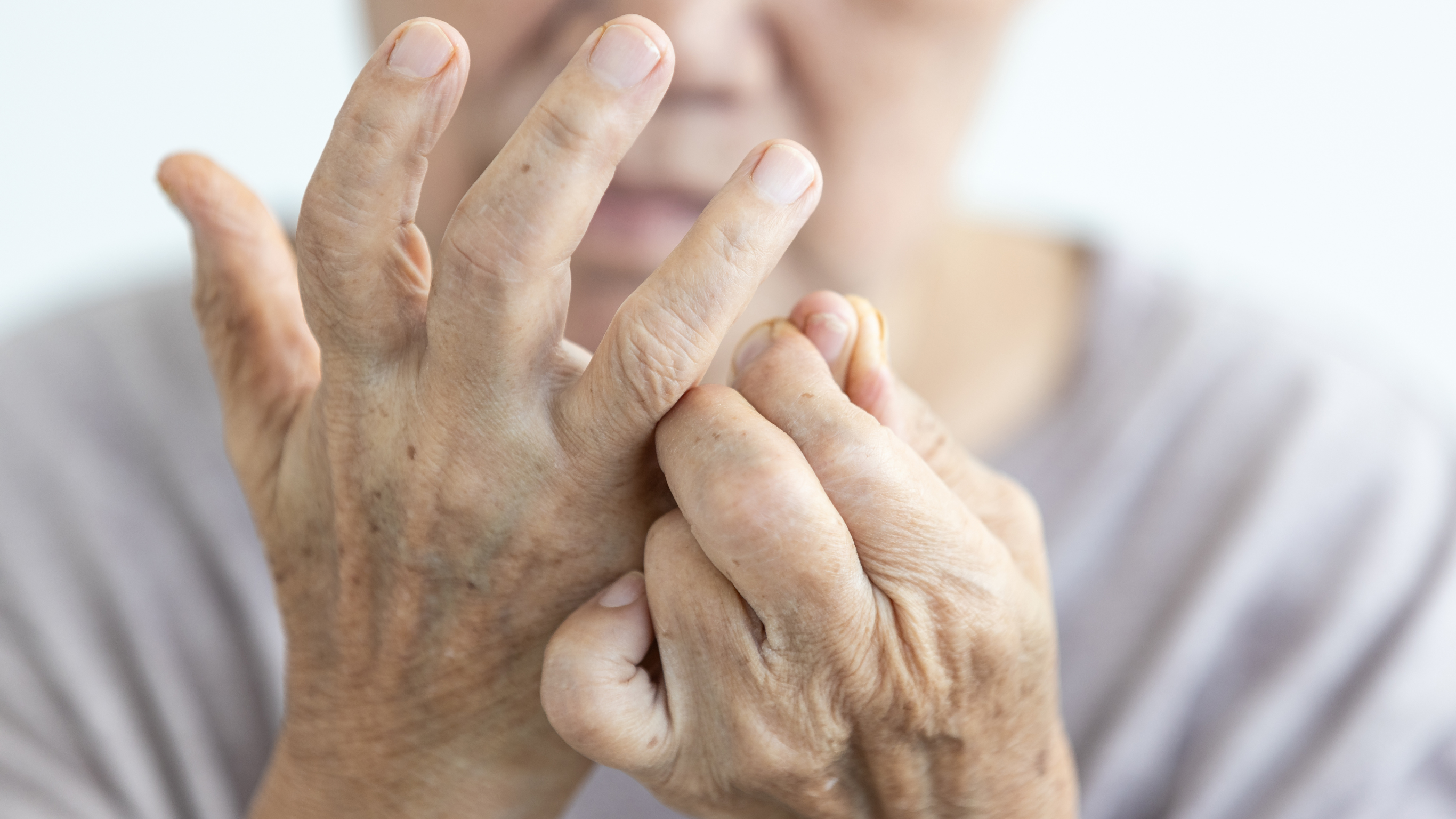
Also known as degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) affects one or more joints in the body and causes the cartilage covering on the bones to wear out gradually.
Osteoarthritis commonly occurs most often in the hips, lower back and neck, knees, thumb and the small joints of fingers.
CMC arthritis (in the thumb joint) is the second most common form of osteoarthritis in the body, and is particularly prevalent in women.
Studies show that over 25% of postmenopausal women have evidence of osteoarthritis at the basal thumb joint.
Osteoarthritis can also affect your wrist. When you strain or fracture your wrist, it can change the anatomy of your wrist and damage the articular cartilage. If the damage is severe and the cartilage becomes damaged, joints can become inflamed and gradually pave the way for wrist osteoarthritis.
What are the symptoms?
Pain is the primary symptom, along with joint stiffness in the mornings, and / or swelling, loss of movement and tenderness.
How is it treated?
Specialist intervention is important for determining the health of your joints, so go and see your doctor if you suspect OA. Your doctor may recommend X-rays to provide detailed images of dense structures like bones. Similarly, blood tests also help to clarify the type of arthritic condition.
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, timely intervention can help reduce the frequency and intensity of symptoms and loss of function. Therapy can also help reduce stress on affected joints and slow the progress of degeneration.
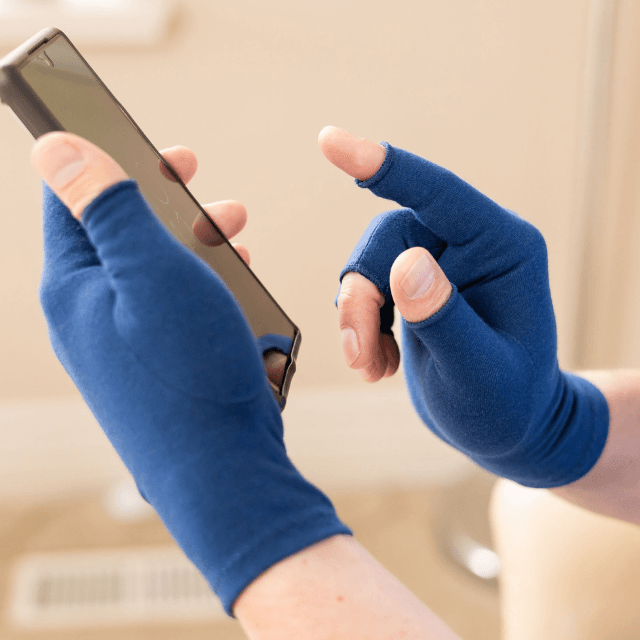
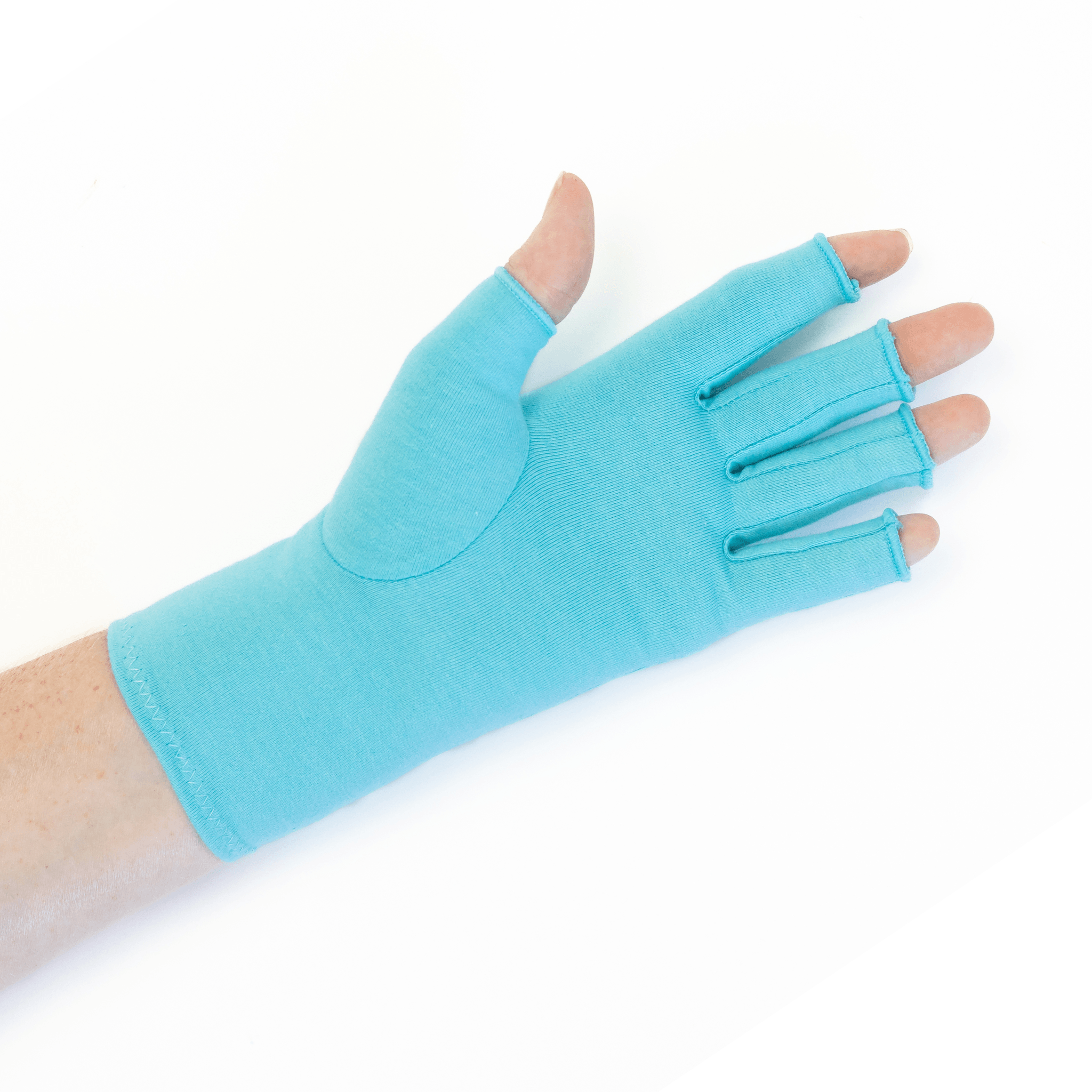
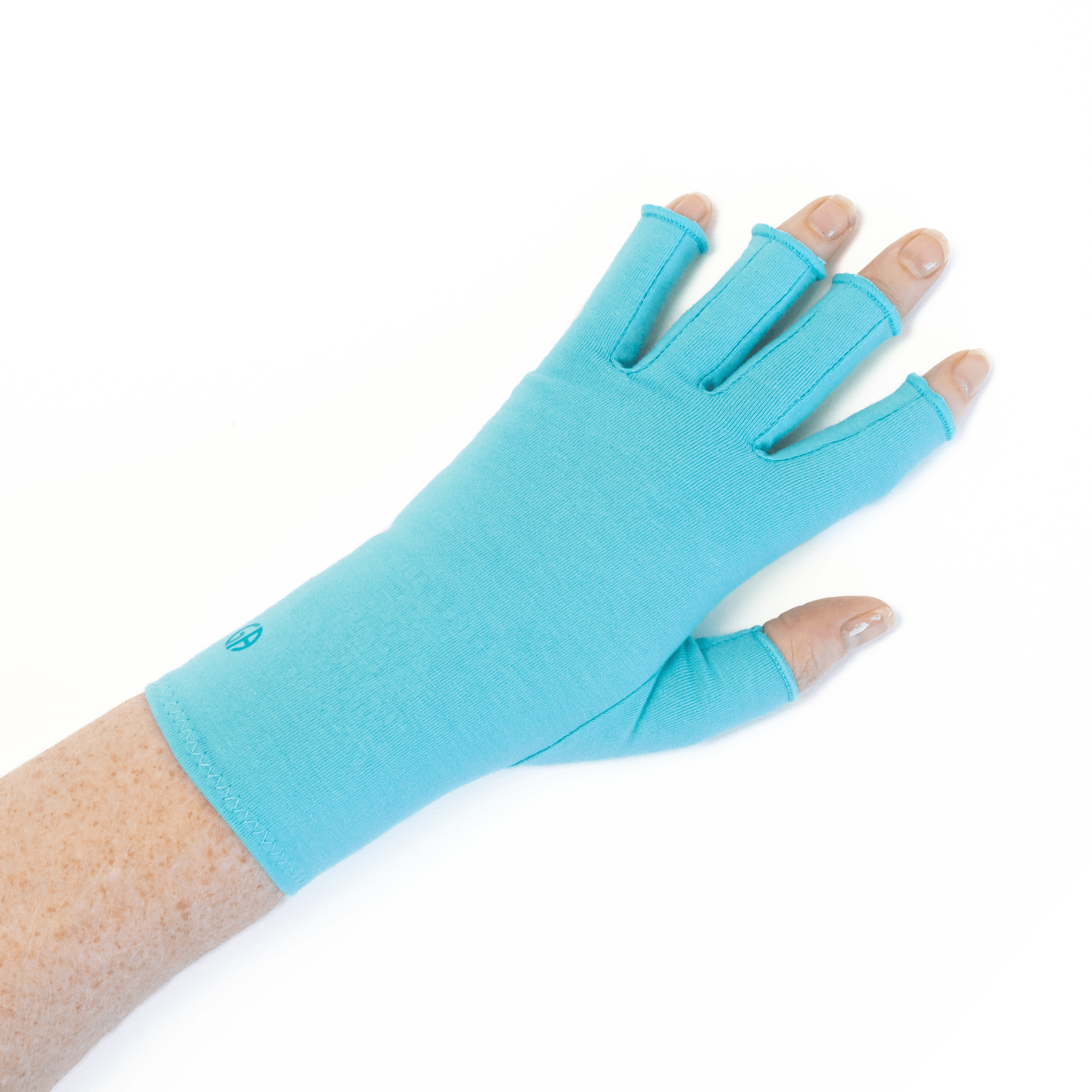
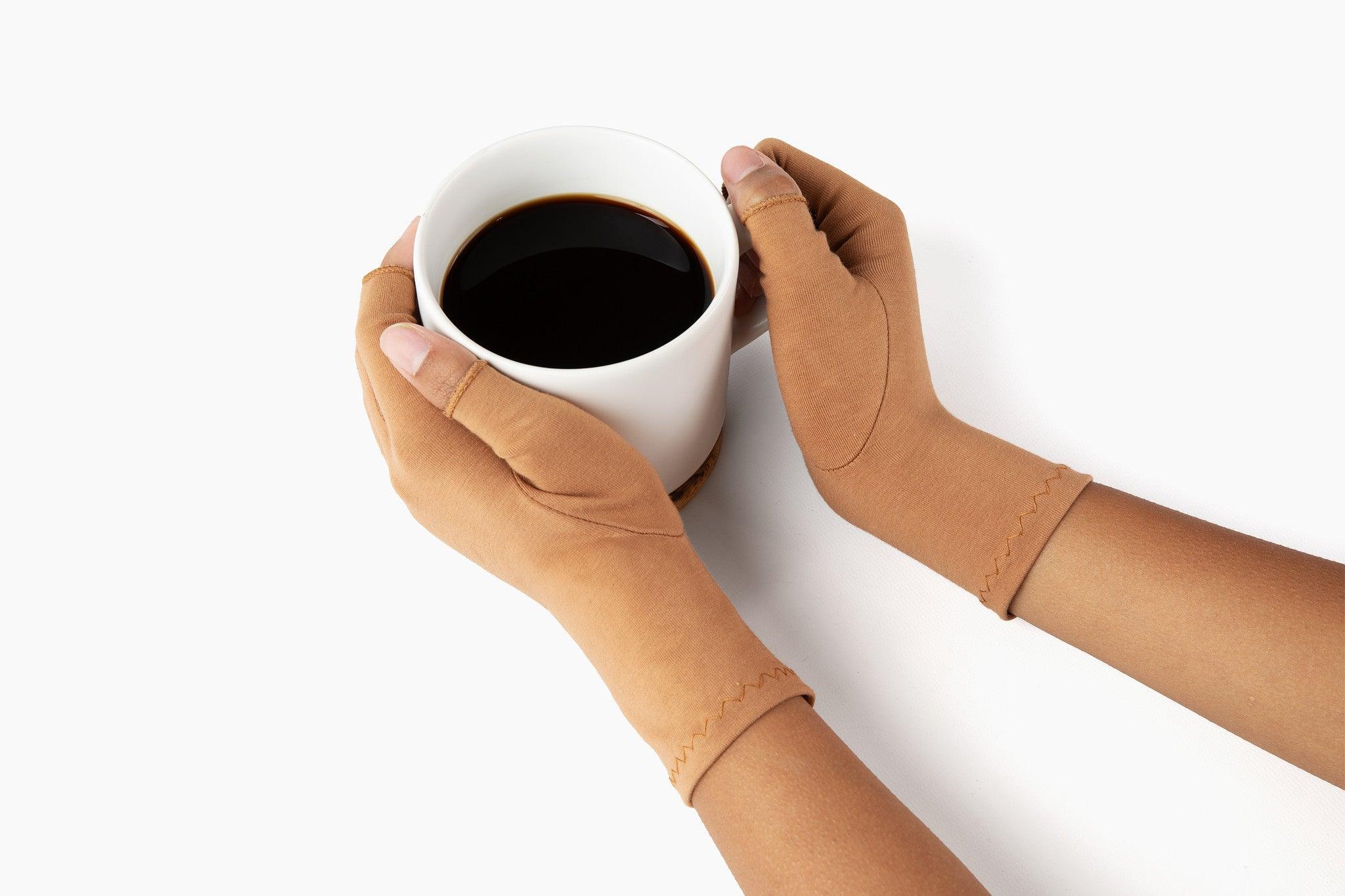
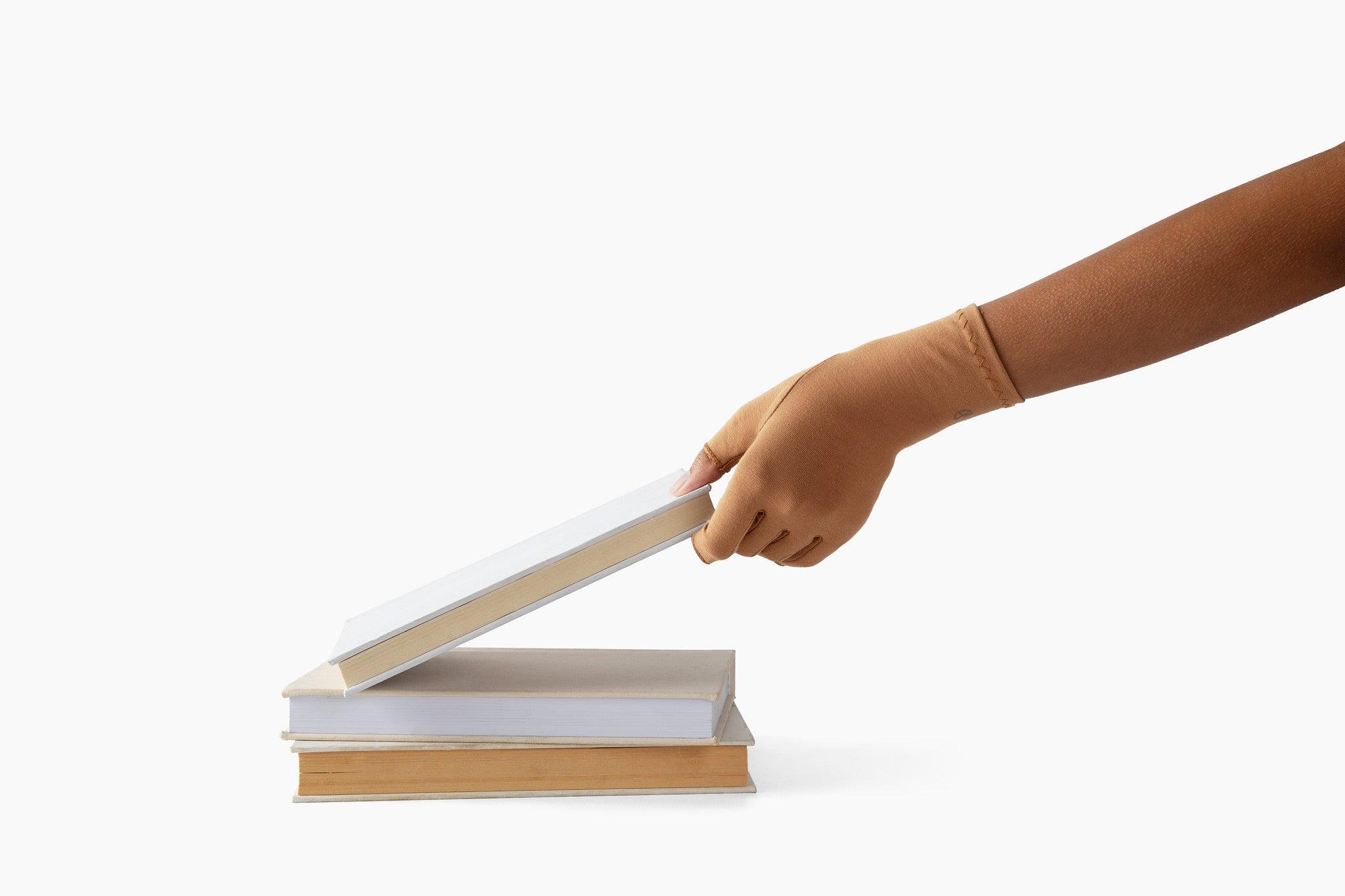
A medical professional may recommend activity modification, exercise, medication, wearing a wrist splint, steroid injections, and the use of warm and/or cold compresses to manage the symptoms better, or even surgery.
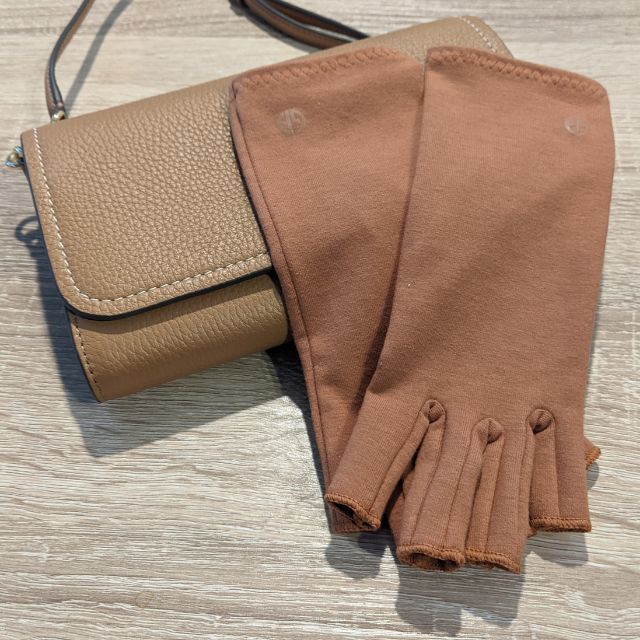
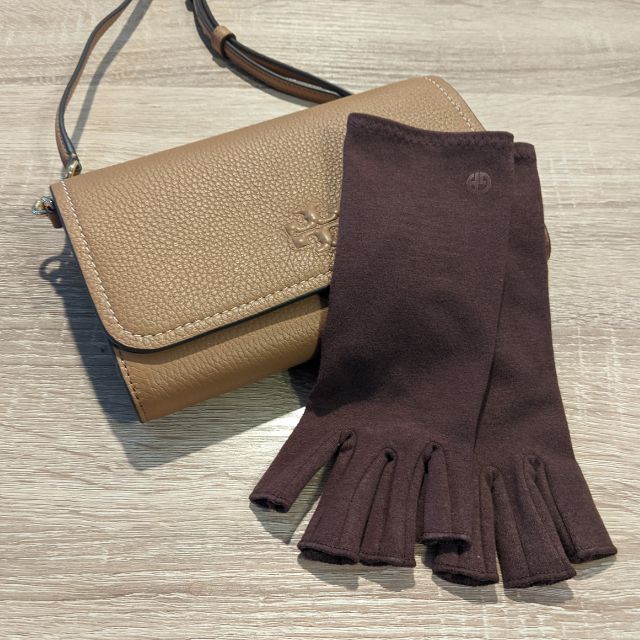
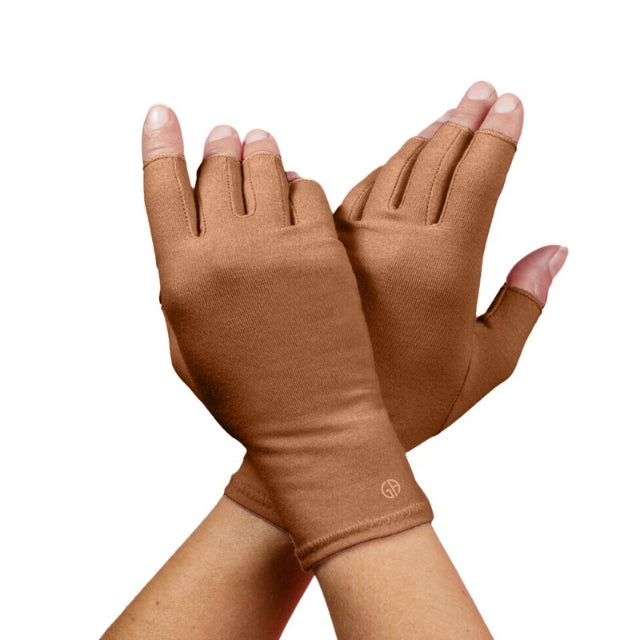
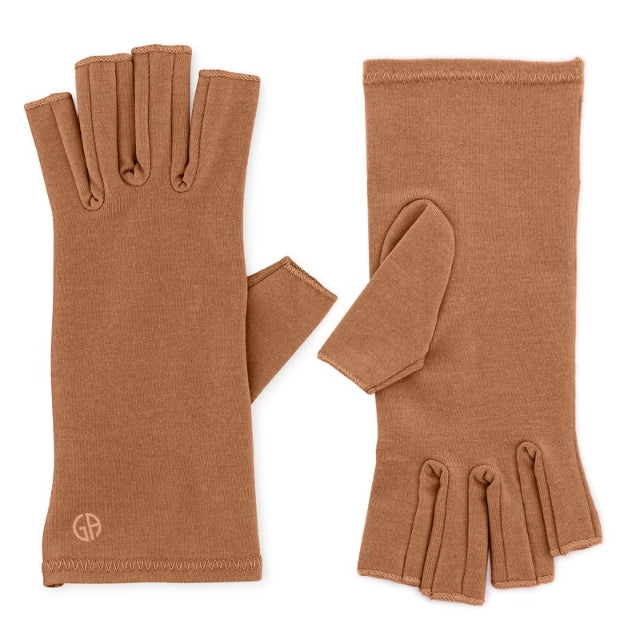









































































Share and get 15% off!
Simply share this product on one of the following social networks and you will unlock 15% off!